Ok, so you may not be highlander fan but let’s face it, there are quite a few abrasives out there and they all do different things. So who do you call to the rescue?
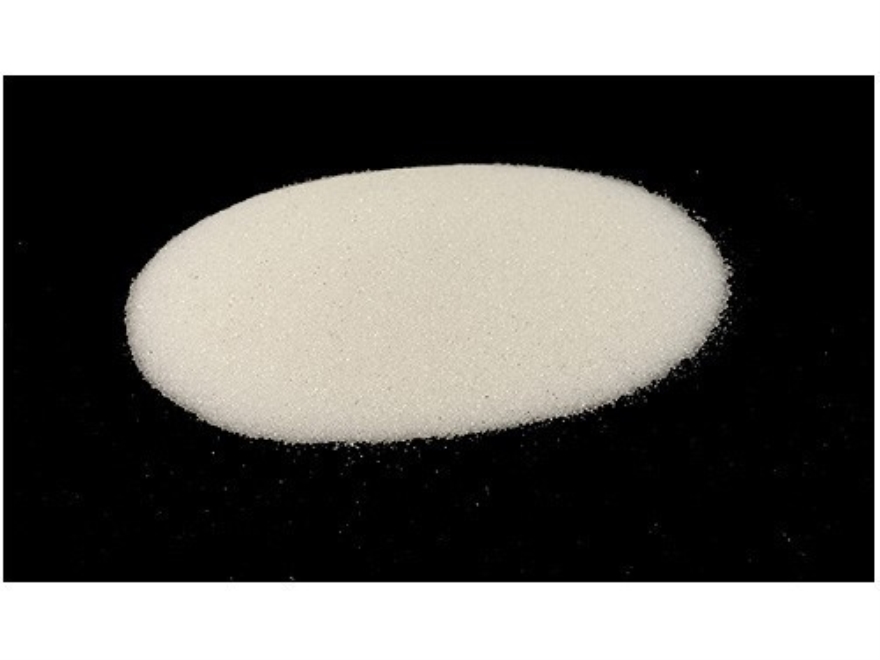
Glass Bead
Typically if you work in the Motorcycle or Automotive restoration business, you may be familiar with Glass Bead. This abrasive will clean metal parts without etching the surface and is typically blasted at 60-90 PSI to achieve the most productive results and produces lower dust levels than most abrasives. This improves operator visibility rates and clean-up costs while providing smooth, polished, or matte finish.
Brown Aluminum Oxide
Removing paint naturally is not only time consuming and tiring, but the chemical process can be a hazard to your health and the environment. Paint stipping chemicals cause headaches, drowsiness, nausea, and have been linked to cancer, reproductive problems and damage to the kidney, liver, and brain. This can cause employees to miss work and therefore slowing down productivity. BAO can also create a more aesthetically pleasing product by deburring machined parts some CNC Machines my not be able to reach and is a more cost-effective option.
Ceramic Bead Abrasive
With a low breakdown rate, ceramic is often compared to glass bead, however, ceramic bead provides a more consistent surface finish over long production runs and have greater toughness and density.

Things to keep in mind
Round circular beads such as glass bear and ceramic beat will roll across the substrate creating a lapping or finishing effect. Other abrasives, however, such as our hero Aluminum Oxide and Ceramic Grit will have sharp angular edges that will flow across the surface scratching and etching the surface which will not only leave the surface shiny but matte and ready for coatings.
Ra and RMS are both representations of surface roughness, but each is calculated differently. Ra stands for roughness average and is the arithmetic average of the absolute value of the profile height deviations from the mean line, recorded within the evaluation length. Ra is measured as the roughness average of surfaces measured by microscopic peaks and valleys. RMS stands for Root Mean Square and is calculated as the Root Mean Square of surfaces measured microscopic peaks and valleys.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]